CompletableFuture
一、回顾 Future
在 Java 之中有哪几种方式可以创建线程呢?
- 继承 Thread 类
- 实现 Runnable 接口
- 实现 Callable 接口
其中 Callable 接口,可以在主线程之中阻塞获取返回结果,而获取返回结果则是通过 Future 类来完成,并且借助这个类还可了解任务执行情况,或者取消任务的执行。我们首先来看一下 Callable 接口的基本使用:
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
log.info("异步任务执行");
return new Random().nextInt();
}
});
executorService.submit(futureTask);
Integer futureTaskRes = futureTask.get();
log.info("异步任务获取到的返回返回结果为:{}", futureTaskRes);除了这种方式,我们还可以直接在 submit 方法之中传入 Callable 接口,通过 submit 方法返回的 Future 获取返回结果
Future<Integer> future = executorService.submit(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
log.info("异步任务执行");
return new Random().nextInt();
}
});
Integer res = future.get();其中,get 方法会阻塞获取结果,但是不推荐使用,更推荐使用下面这个方法:
public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)除了阻塞式获取返回结果,还可以通过如下方式进行轮询的方式进行获取,但是这种方式,会浪费 CPU
Future<Integer> future = executorService.submit(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
log.info("异步任务执行");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
return new Random().nextInt();
}
});
while (true) {
if(future.isDone()) {
log.info("异步任务执行完成 {}", future.get());
break;
}
}二、CompletableFuture
在 JDK8 开始,对于 Future 进行了改进,提出了 CompletableFuture,简化了异步编程的复杂性,可以通过回调的方式处理计算结果,并且可以转化和组合 CompletableFuture 的方法
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> {}从接口的继承关系来看,CompletableFuture 是对 Future 的扩展,Future 接口具备的功能在 CompletableFuture 接口仍然存在。
CompletionStage 接口代表异步计算过程之中的某个阶段,一个阶段完成之后,以后可能会触发另外一个阶段
2.1 构造异步任务
通过 CompletableFuture 来构建异步任务,有两种方式:
- runAsync:没有返回结果
- supplyAsync:有返回结果
2.1.1 runAsync
CompletableFuture<Void> futureByRunnable = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
log.info("completableFutureByRunnable execute");
});
futureByRunnable.get();ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
CompletableFuture<Void> futureByRunnableByRunnableAndExecutor = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
log.info("futureByRunnableByRunnableAndExecutor execute");
}, executorService);
futureByRunnableByRunnableAndExecutor.get();
executorService.shutdownNow();对应的输出结果如下:

从这里我们能够看到,如果不指定线程池,默认直接使用 ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为默认的线程池
2.1.2 supplyAsync
CompletableFuture<Integer> futureBySupplyAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("futureBySupplyAsync execute");
return new Random().nextInt();
});
Integer futureBySupplyAsyncRes = futureBySupplyAsync.get();
log.info("futureBySupplyAsync - Res = {}" , futureBySupplyAsyncRes);ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
CompletableFuture<Integer> futureBySupplyAsyncExecutor = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("futureBySupplyAsyncExecutor execute");
return new Random().nextInt();
}, executorService);
Integer futureBySupplyAsyncExecutorRes = futureBySupplyAsyncExecutor.get();
log.info("futureBySupplyAsyncExecutor - Res = {}" , futureBySupplyAsyncExecutorRes);
executorService.shutdownNow();对应的输出结果如下:

2.2 异步回调
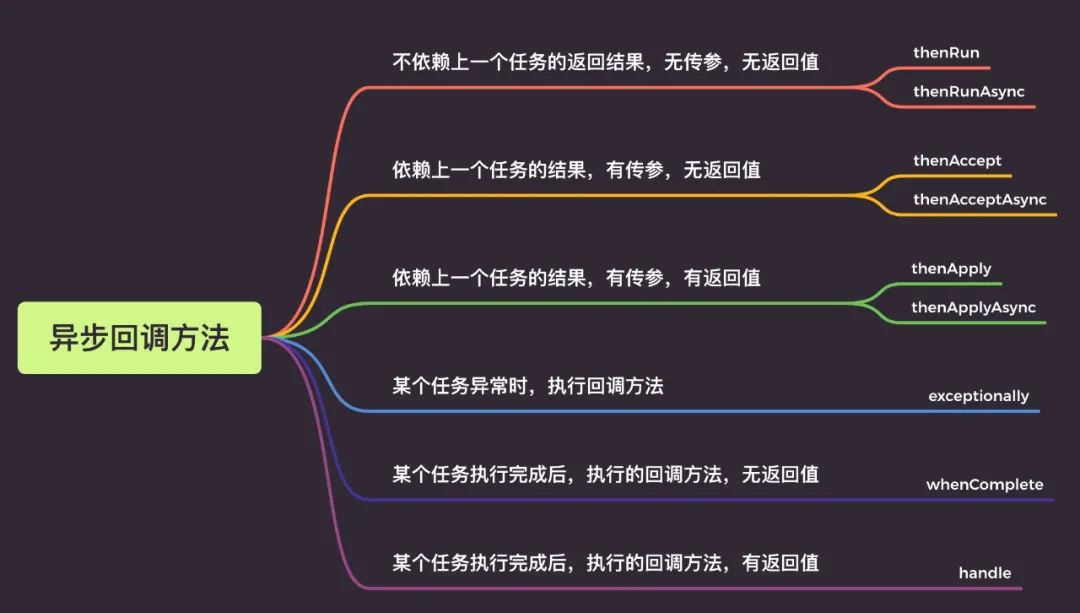
2.2.1 thenRun/thenRunAsync
作用:执行完成第一个任务之后,然后再开始第二个任务,两个任务直接没有参数的参数
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(null, action);
}
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(asyncPool, action);
}对应的示例如下:
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("1.1 execute");
return 1;
}).thenRun(() -> {
log.info("1.2 execute");
});CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("2.1 execute");
return 1;
}).thenRunAsync(() -> {
log.info("2.2 execute");
});那么这两个方法,有什么区别吗?
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(null, action);
}
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(asyncPool, action);
}2.2.2 thenAccept/thenAcceptAync
第一个 任务执行完成之后,会调用第二个任务,并且将第一个任务的返回结果作为入参,返回给第二个任务
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action) {
return uniAcceptStage(null, action);
}
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action) {
return uniAcceptStage(asyncPool, action);
}
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,
Executor executor) {
return uniAcceptStage(screenExecutor(executor), action);
}